这篇文章主要讲解了“pytorch怎么实现梯度下降和反向传播”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“p...
这篇文章主要讲解了“pytorch怎么实现梯度下降和反向传播”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“pytorch怎么实现梯度下降和反向传播”吧!
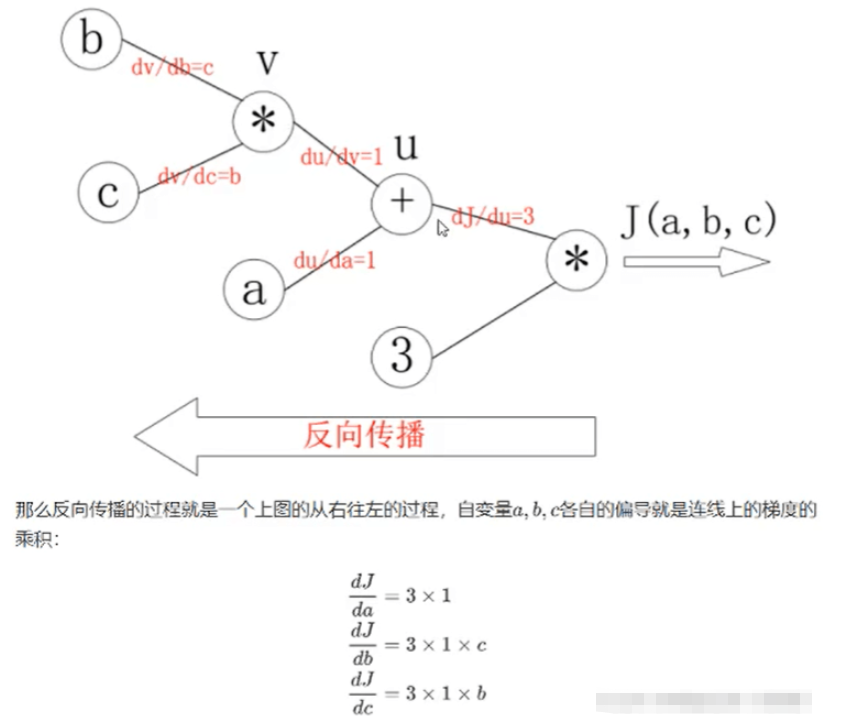
反向传播
这里说一下我的理解,反向传播是相对于前向计算的,以公式J(a,b,c)=3(a+bc)为例,前向计算相当于向右计算J(a,b,c)的值,反向传播相当于反过来通过y求变量a,b,c的导数,如下图
手动完成线性回归
import torch
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
"""
假设模型为y=w*x+b
我们给出的训练数据是通过y=3*x+1,得到的,其中w=3,b=1
通过训练y=w*x+b观察训练结果是否接近于w=3,b=1
"""
# 设置学习率
learning_rate=0.01
#准备数据
x=torch.rand(500,1) #随机生成500个x作为训练数据
y_true=x*3+1 #根据模型得到x对应的y的实际值
#初始化参数
w=torch.rand([1,1],requires_grad=True) #初始化w
b=torch.rand(1,requires_grad=True,dtype=torch.float32) #初始化b
#通过循环,反向传播,更新参数
for i in range(2000):
# 通过模型计算y_predict
y_predict=torch.matmul(x,w)+b #根据模型得到预测值
#计算loss
loss=(y_true-y_predict).pow(2).mean()
#防止梯度累加,每次计算梯度前都将其置为0
if w.grad is not None:
w.grad.data.zero_()
if b.grad is not None:
b.grad.data.zero_()
#通过反向传播,记录梯度
loss.backward()
#更新参数
w.data=w.data-learning_rate*w.grad
b.data=b.data-learning_rate*b.grad
# 这里打印部分值看一看变化
if i%50==0:
print("w,b,loss:",w.item(),b.item(),loss.item())
#设置图像的大小
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8))
#将真实值用散点表示出来
plt.scatter(x.numpy().reshape(-1),y_true.numpy().reshape(-1))
#将预测值用直线表示出来
y_predict=torch.matmul(x,w)+b
plt.plot(x.numpy().reshape(-1),y_predict.detach().numpy().reshape(-1),c="r")
#显示图像
plt.show()pytorch API完成线性回归
优化器类
优化器(optimizer),可以理解为torch为我们封装的用来进行更新参数的方法,比如常见的随机梯度下降(stochastic gradient descent,SGD)
优化器类都是由torch.optim提供的,例如
torch.optim.SGD(参数,学习率)
torch.optim.Adam(参数,学习率)
注意:
①实例化
②所有参数的梯度,将其置为0
③反向传播计算梯度
④更新参数值
实现
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch import optim
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# 1.定义数据,给出x
x=torch.rand(50,1)
# 假定模型为y=w*x+b,根据模型给出真实值y=x*3+0.8
y=x*3+0.8
# print(x)
#2.定义模型
class Lr(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Lr, self).__init__()
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(1, 1)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.linear(x)
return out
# 3.实例化模型、loss、优化器
model=Lr()
criterion=nn.MSELoss()
# print(list(model.parameters()))
optimizer=optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=1e-3)
# 4.训练模型
for i in range(30000):
out=model(x) #获取预测值
loss=criterion(y,out) #计算损失
optimizer.zero_grad() #梯度归零
loss.backward() #计算梯度
optimizer.step() #更新梯度
if (i+1)%100 ==0:
print('Epoch[{}/{}],loss:{:.6f}'.format(i,30000,loss.data))
# 5.模型评估
model.eval() #设置模型为评估模式,即预测模式
predict=model(x)
predict=predict.data.numpy()
plt.scatter(x.data.numpy(),y.data.numpy(),c="r")
plt.plot(x.data.numpy(),predict)
plt.show()感谢各位的阅读,以上就是“pytorch怎么实现梯度下降和反向传播”的内容了,经过本文的学习后,相信大家对pytorch怎么实现梯度下降和反向传播这一问题有了更深刻的体会,具体使用情况还需要大家实践验证。这里是捷杰建站,小编将为大家推送更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注!